Prolonged QT interval (Hypocalcaemia)
 | ||
| A prolonged Q-T interval refers to an abnormality seen on an electrocardiogram that reflects a disturbance in how your heart conducts electricity. [Source] |
 |
| Long QT interval [Source] |
The QT interval normally varies with heart rate - becoming shorter at faster rates. It is usually corrected using the cycle length (R-R interval) as shown opposite.
Normal QTc = 0.42 seconds
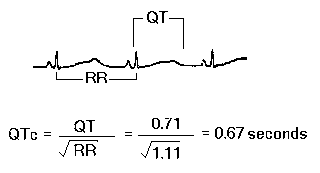 |
| QTc calculation [Source] |
Tall T waves (Hyperkalaemia)
The following changes may be seen in hyperkalaemia
- Small or absent P waves
- Atrial fibrillation
- Wide QRS
- Shortened or absent ST segment
- Wide, tall and tented T waves
- Ventricular fibrillation
 |
| ECG changed in hyperkalaemia. [Source] |
No comments:
Post a Comment